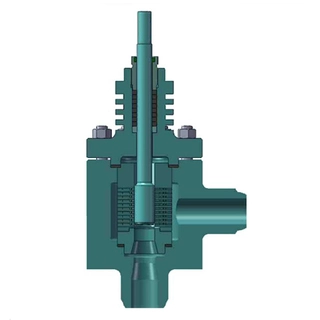
An angle control valve features inlet and outlet ports at a 90-degree angle, enabling space-efficient installation. Operating similarly to a globe valve, it regulates fluid flow using a linear motion plug against a seat. Widely used in tight spaces or when flow direction needs redirection, angle control valves offer reliable throttling and shutoff capabilities, suitable for HVAC, water treatment, and chemical processing applications.
An angle control valve, often referred to as an angle valve or angle body valve, is a specialized type of control valve designed to regulate the flow of fluids or gases in a system. Its distinctive feature is an angled body design, which facilitates precise control over the flow, making it ideal for applications requiring accuracy and reliability.
These valves play a pivotal role in critical systems such as discharge pipelines between autoclaves and flash tanks in oxygen pressure leaching workshops. By ensuring stable device operation, they contribute to maintaining production efficiency and minimizing costs.
Angle control valves are essential in industries like mining, smelting, and chemical processing. Their robust design allows them to withstand harsh conditions and resist erosion, making them a preferred choice for pipelines in these sectors. Companies like Weidouli Valves have developed angle control valves with advanced structural and material designs to meet diverse customer requirements.
One of the key strengths of angle control valves is their ability to handle high-pressure and high-flow scenarios, which makes them suitable for industries such as:
Regulating the flow of steam, water, and other fluids ensures proper pressure levels, safeguarding equipment and personnel from overpressure hazards.
Managing oil and gas flow at various production stages, from wellhead extraction to transportation and usage, helps maintain optimal pressure and flow, preventing damage and enhancing safety.
Controlling chemical and gas flow with precision supports safe processing, protecting both equipment and personnel from hazardous conditions.
Ensuring water enters and exits treatment processes at correct pressures improves efficiency and protects systems from damage.
Angle control valves come in two primary types, each suited for specific applications:
Featuring a linear flow path, globe valves use a cylindrical plug that moves vertically to control flow. They are known for their accuracy and are ideal for precise flow regulation.
With a circular flow path, rotary valves use a rotating disc or vane to manage fluid or gas flow. These valves offer versatility and are often chosen for applications where compact design and efficient flow are critical.
Both types can be actuated through various mechanisms, including manual operation, pneumatic systems, hydraulic systems, and electric actuators.
Anti-Erosion Performance: Engineered to resist wear from harsh conditions, ensuring long-term reliability.
Supports multiple actuation methods, including pneumatic, hydraulic, and electric, to suit different operational requirements.
Advanced material selection and structural designs enhance performance and durability in demanding applications.
Designed for precise regulation, providing consistent performance across varied conditions.
Material choice plays a critical role in the durability and efficiency of angle control valves. Common materials include:
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant and suitable for harsh environments.
Bronze and Brass: Used for specific applications requiring durability and moderate cost.
Specialized Alloys: Developed to handle extreme pressures, temperatures, or erosive environments.
The angled body of these valves reduces pressure drop and ensures smoother flow characteristics. Additional design elements, such as contra-vanes and anti-erosion features, further enhance their effectiveness in challenging applications.