In an era where cleanliness, precision, and automation are paramount across food, beverage, pharmaceutical, biotech, and other sanitary industries, pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves have become essential components in fluid handling systems. Combining hygienic design principles with pneumatic actuation, these valves offer reliability, speed, and operational excellence, meeting stringent regulatory requirements while optimizing process efficiency.
This in-depth news feature explores the technology behind pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves, their design advantages, key applications, industry trends, global market dynamics, technical considerations, compliance standards, and future outlook.
Pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves are specialized quarter-turn valves designed to control fluid flow in hygienic and sterile environments. What distinguishes them from standard valves is:
- Sanitary design: Bodies, discs, and seats are crafted to minimize crevices and contamination risks. Materials such as stainless steel (e.g., 316/316L) ensure corrosion resistance and cleanability.
- Pneumatic actuation: Instead of manual handles, these valves use pneumatic actuators (single-acting or double-acting) powered by compressed air to open or close the valve. Pneumatic actuation enables remote operation and integration with automated systems.
- Biopharmaceutical and food-grade compatibility: Seals and elastomers are selected for compliance with food safety and pharmaceutical purity standards (e.g., FDA, USP Class VI).
In practice, a pneumatic sanitary butterfly valve consists of a circular disc that rotates around a shaft to regulate flow. Rotating the disc 90° shifts the valve from fully open to fully closed, with throttling capabilities for intermediate positions when using intelligent control systems.
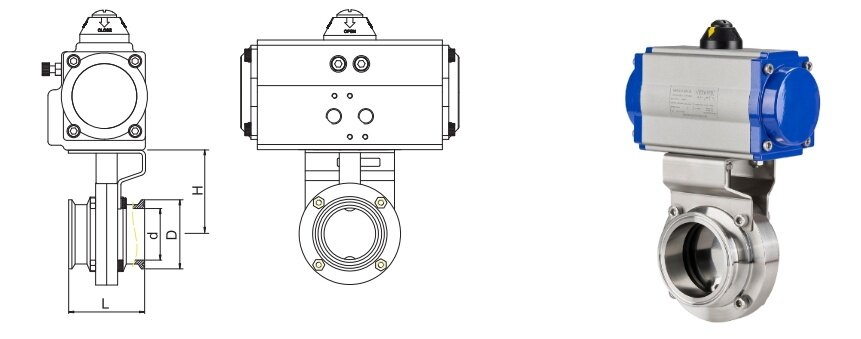
The valve body is the skeleton of the butterfly valve. For sanitary applications it is typically manufactured from high-grade stainless steel (e.g., 316L) that offers:
- Passive corrosion resistance
- Polished surfaces to resist bacterial adherence
- Welded or clamp-style connections for hygienic installation
The disc — also polished and balanced — rotates within the body. Its design minimizes dead zones where fluid might stagnate.
Sanitary seals and seats are frequently made from FDA-approved elastomers like EPDM, PTFE, or silicone. These materials provide:
- Chemical compatibility
- Thermal stability
- Excellent sealing to prevent leaks
Depending on application pressures and required cleanability, seat designs may be solid, encased in metal, or self-energizing.
Pneumatic actuation brings automation capabilities. Two main types are used:
- Single-acting (spring return): Uses compressed air to open or close the valve, with a spring to return it to the default position upon air loss.
- Double-acting: Relies on compressed air for both opening and closing, enabling more controlled operation suited to frequent cycling.
Pneumatic actuators are valued because they:
- Operate rapidly
- Are inherently safe in harsh environments (e.g., wet, high humidity)
- Are easy to integrate with control systems
Advanced installations often include digital or analog positioners to modulate valve position, enabling precise flow control. Smart controllers can communicate status and diagnostics, feeding into SCADA systems or PLCs for optimized plant automation.
Across sanitary process industries, performance objectives include:
- Product purity and safety
- High throughput and minimal downtime
- Ease of cleaning and sterilization
- Automation and remote operation
Pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves answer all these needs, offering:
- Clean-in-Place (CIP) and Sterilize-in-Place (SIP) compatibility: Their smooth surfaces and minimal crevices ensure rapid rinsing and sterilization without disassembly.
- Fast cycling: Pneumatic actuation enables much faster operation than manual alternatives, critical in automated production lines.
- Reduced contamination risk: Hygienic designs minimize fluid entrapment and bacterial growth.
These valves serve as backbone components in production lines where even trace contamination can cause product rejection or regulatory compliance issues.
In food production, sanitary valves maintain product quality and safety. Pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves are used in:
- Dairy processing (milk, yogurt, cheese)
- Brewing and beverage production
- Sauces, syrups, and liquid food processing
- Bottling and packaging systems
Their ease of cleaning and compliance with food sanitation standards make them indispensable.
Pharmaceutical processes demand sterile fluid pathways and traceability. Pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves are key to:
- Bioreactors and fermentation systems
- Buffer and media transfer lines
- Purified water distribution
- Parenteral drug manufacturing
Controlled actuation maintains sterility while eliminating human error in critical procedures.
Viscous fluids such as lotions, creams, and gels require valves that:
- Achieve tight shut-off
- Resist product buildup
- Permit easy cleaning
Sanitary pneumatic valves help maintain product consistency and hygiene standards.
Certain specialty chemicals that must be handled in cleaner environments also benefit from corrosion-resistant sanitary valves with automated actuation control.
Compared to manual or non-sanitary valves, pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves deliver multiple operational advantages:
The polished internals and sanitary connections reduce microbial entrapment. They are fully compatible with:
- CIP flushing (with detergents and high-temperature water)
- SIP steam sterilization
Manual valves often involve handles and seals that complicate cleaning.
Remote actuation via pneumatics connects seamlessly to modern production controls, enabling automatic shutdowns, flow adjustments, and emergency interlocks — crucial for modern Industry 4.0 manufacturing.
Pneumatic actuation can complete open/close cycles in seconds, significantly reducing processing pauses. Manual operation simply cannot match this speed, especially under high throughput scenarios.
Although pneumatically actuated sanitary valves involve higher upfront costs than manual ones, they reduce:
- Labor costs (less manual intervention)
- Downtime (automated safety responses)
- Product loss (precise shut-off prevents spillage)
Sanitary pneumatic valves are subject to rigorous standards and compliance requirements:
- FDA and EC Regulation: Sealing materials must be compliant with food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade specifications.
- 3A Sanitary Standards: Common in North American food and dairy industries.
- USP Class VI: Required for pharmaceutical elastomers.
- CE marking and ATEX: When pneumatic control systems operate in regulated markets or hazardous areas.
Sanitary valves often specify internal finishes in micro-inch roughness (e.g., <32 µin / 0.8 µm) to prevent microbial harborage.
End users increasingly demand traceability — often requiring mill test certificates (MTC), material trace records, and validation documentation for critical processes.
Multiple market forces are driving increased adoption of pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves:
Across food, beverage, and pharmaceutical lines, Industry 4.0 adoption means automated control systems — which rely on actuated valves.
As demand for safer, cleaner products rises, so does investment in hygienic fluid handling infrastructure.
Producers are shifting toward flexible platforms capable of rapid line changeovers. Pneumatic sanitary valves support quick reconfiguration without compromising hygiene.
Pneumatic systems often require less maintenance and leak less than alternatives — supporting environmental goals and operational resilience.
Despite their advantages, pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves face some challenges:
Pneumatic actuation requires a clean, dry compressed air supply. Poor air quality can degrade actuator performance.
Solution: Installing proper air filtration and dryers ensures consistent control and extends actuator lifetime.
Integration with control systems adds complexity.
Solution: Using smart positioners with digital communication (e.g., HART, Modbus, ProfiNet) simplifies networking and diagnostics.
Some elastomers may not withstand extreme chemicals or temperatures.
Solution: Selecting appropriate seat materials (e.g., PTFE for chemical resistance) and designing valves with thermal insulation address specific process conditions.
A major dairy producer modernized its processing line by replacing manual butterfly valves with pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves featuring double-acting actuators and digital positioners. Results included:
- 30% reduction in cleaning time
- Improved product quality consistency
- Zero contamination incidents over a 6-month period
In a biotech facility producing monoclonal antibodies, pneumatic valves integrated with PLC systems enabled precise buffer transfer control, improving:
- Cycle times by 20%
- Regulatory compliance visibility via SCADA logs
- Reduction in manual operator interventions
A beverage manufacturer deployed a modular fluid handling line using sanitary pneumatic valves. The ability to reconfigure lines rapidly supported seasonal product changes and reduced downtime.
Selecting the right valve requires careful review of:
- Flow rates and pressure ranges
- Temperature extremes
- Type of fluid (viscosity, particulates, pH)
- Degree of polish
- Cleanability and sterilization needs
- Regulatory compliance
- Frequency of operation
- Integration with plant automation
- Feedback requirements (position sensors)
- Availability of spare parts
- Local service support
- Documentation and validation packages
As manufacturing evolves, pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves are also transforming:
Sensor integration enables real-time monitoring of valve health, predicting maintenance needs before failures.
Valves equipped with smart positioners can communicate over secure networks, feeding data for optimization and compliance reporting.
Next-generation valve actuators aim to reduce compressed air consumption — improving sustainability.
Combining pneumatics with electric or electro-pneumatic hybrid systems offers finer control with lower energy footprints.
Industry leaders emphasize the importance of hygienic design coupled with automation. According to a process engineer specializing in sanitary systems:
“Pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves strike a balance between cleanability and automation. Their ability to integrate with modern control systems while maintaining strict hygiene makes them indispensable in today’s high-efficiency facilities.”
Quality assurance managers also report that automated pneumatic actuation reduces human variability — a major factor in contamination prevention.
|
Standard / Regulation |
Industry |
Focus |
|
3A Sanitary Standards |
Food & Dairy |
Hygienic design criteria |
|
FDA 21 CFR |
Food/Pharma |
Material safety compliance |
|
USP Class VI |
Pharma |
Biological safety of elastomers |
|
CE / ATEX |
Global |
Safety/Electrical/Explosion |
|
ISO 5211 |
Industrial |
Actuator mounting standards |
Sanitary pneumatic butterfly valves contribute to sustainability by:
- Reducing downtime: Automated control decreases production interruptions.
- Lower product waste: Precision shut-off minimizes spillage.
- Maintenance optimization: Fewer manual adjustments mean lower labor costs.
Environmentally conscious manufacturers are adopting advanced pneumatic solutions designed for minimal air consumption and longer service intervals.
Pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves are no longer optional components; they are central to modern, hygienic, and automated fluid processing systems. As the demands for cleaner products, faster production, and tighter quality controls rise across industries, so does the reliance on precision valve technology.
Manufacturers planning new installations or retrofits should weigh:
- Hygienic design requirements
- Actuation and automation needs
- Regulatory compliance
- Lifecycle costs and support
By embracing pneumatic sanitary butterfly valves, producers unlock higher productivity, improved safety, and long-term operational resilience.
