What is a Control Valve?
On this page
What is a control valve? At its core, a control valve is a power-operated device used to regulate or manipulate the flow of fluids, including gas, oil, water, and steam. It is a critical component in various industrial processes, ensuring precise control over fluid flow and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Control valves are essential in control loops, serving as final control elements that receive commands from controllers and adjust fluid flow accordingly. Their ability to accurately control fluid dynamics makes them indispensable in industries ranging from oil and gas to water treatment and power generation.
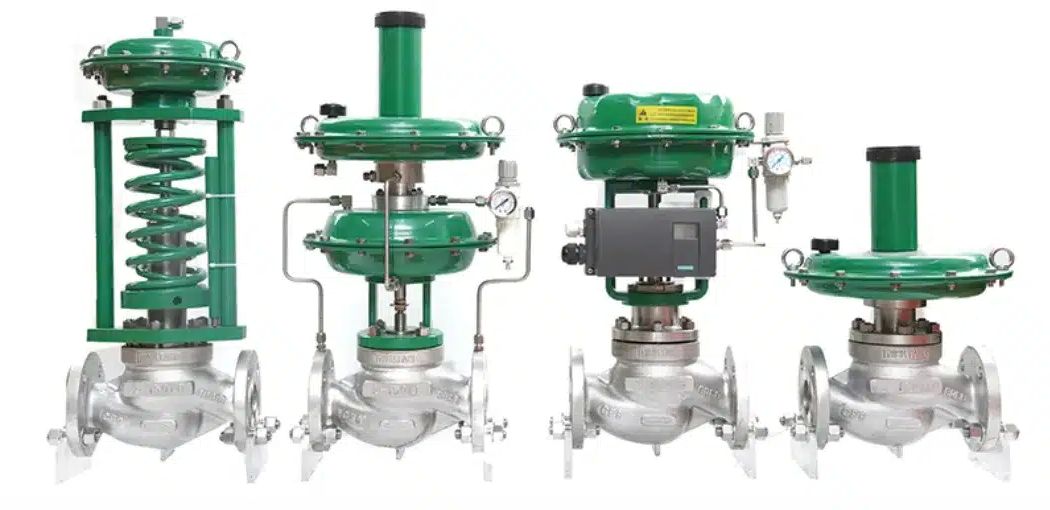




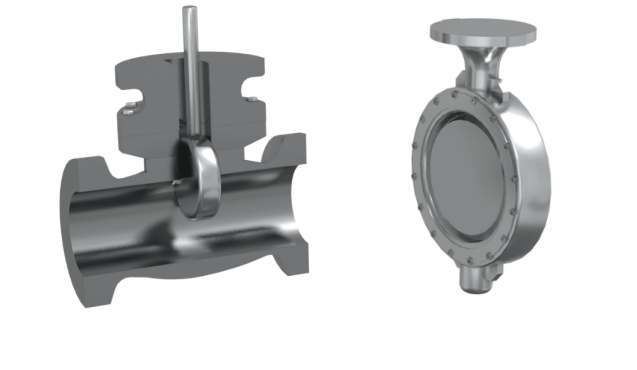
Linear Motion: Valves with linear motion move the valve plug in a straight line to open or close the valve. Examples include globe valves and gate valves.
Rotary Motion: Valves with rotary motion rotate the valve plug to control flow. Examples include ball valves and butterfly valves.
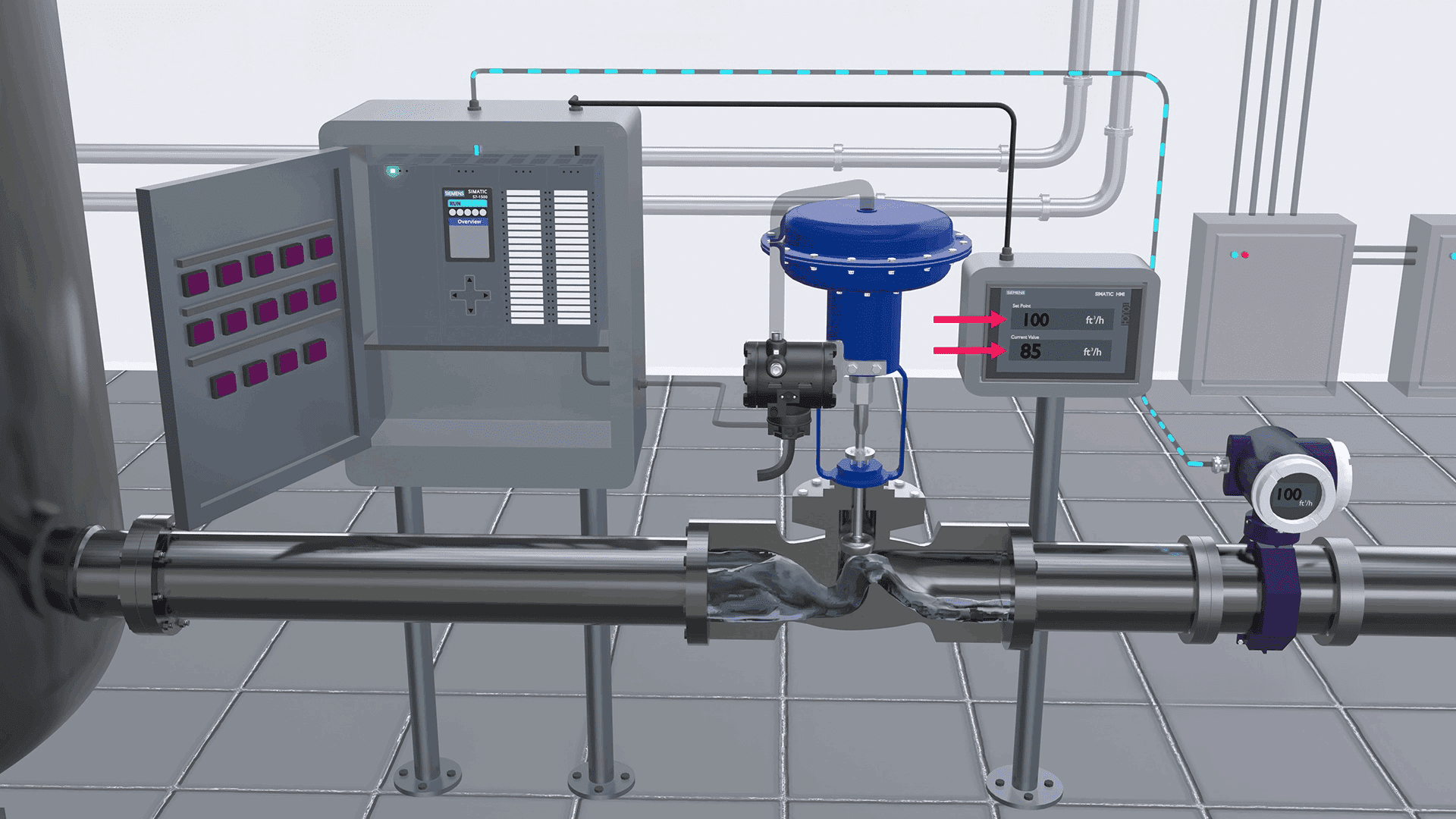
When the controller detects a discrepancy between the actual flow rate and the setpoint, it generates an output signal. This signal is sent to the control valve actuator, instructing it to move the valve accordingly. By adjusting the valve position, the flow rate is brought back to the setpoint value, ensuring the process operates within the desired parameters.
This precise regulation is crucial in maintaining process efficiency, safety, and product quality. For instance, in a chemical processing plant, accurate control of fluid flow is essential to ensure the correct mixing ratios of reactants, leading to the desired chemical reactions and product consistency.
Control valves are the most common final control elements used in industry today, owing to their versatility and reliability. They find applications in numerous sectors, including: Control valves regulate the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products through pipelines, ensuring safe and efficient transportation and processing. In water treatment plants, control valves manage the flow of water through various treatment stages, ensuring clean and safe water supply. Control valves play a crucial role in power plants, controlling the flow of steam and cooling water to maintain optimal operating conditions and efficiency. Precise control of fluid flow in chemical plants is vital for accurate mixing, reaction control, and product consistency.
The importance of control valves in these industries cannot be overstated. They enhance process efficiency, ensure safety, and contribute to overall operational excellence. Control valves are indispensable in modern industrial processes, providing the necessary control over fluid flow to maintain optimal operating conditions. Their ability to accurately regulate fluids such as gas, oil, water, and steam makes them a critical component in various sectors. With advancements in actuator technology and control systems, control valves continue to evolve, offering even greater precision and reliability in industrial applications. Understanding their operation and components is essential for anyone involved in the field of industrial automation and process control.

Control Valves
Control valves comprise several vital components, each playing a unique role in the valve's functionality. Understanding these components is crucial to grasping how control valves operate and their significance in industrial processes.
Actuators are the driving force behind control valves, providing the necessary power to move the valve. There are three primary types of actuators:
These use compressed air to move the valve stem and adjust the flow. Pneumatic actuators are known for their simplicity, reliability, and quick response times.
Pneumatic Actuators
Powered by electricity, these actuators offer precise control and are suitable for applications requiring accurate positioning.
Electric Actuators
Utilizing pressurized fluid, hydraulic actuators provide high force and are ideal for heavy-duty applications where substantial power is needed to operate the valve.
Hydraulic Actuators
The body of the control valve is the main housing that contains the internal components. Control valve bodies can be categorized based on their motion:Linear Motion: Valves with linear motion move the valve plug in a straight line to open or close the valve. Examples include globe valves and gate valves.
Rotary Motion: Valves with rotary motion rotate the valve plug to control flow. Examples include ball valves and butterfly valves.

Linear Motion vs Rotary Motion
The operation of control valves involves a seamless interaction between the valve, a controller, and the process it regulates. The process begins with the controller, which can be a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) or a Distributed Control System (DCS). The controller continuously monitors the actual flow rate of the fluid and compares it to the desired flow value, known as the setpoint.When the controller detects a discrepancy between the actual flow rate and the setpoint, it generates an output signal. This signal is sent to the control valve actuator, instructing it to move the valve accordingly. By adjusting the valve position, the flow rate is brought back to the setpoint value, ensuring the process operates within the desired parameters.
This precise regulation is crucial in maintaining process efficiency, safety, and product quality. For instance, in a chemical processing plant, accurate control of fluid flow is essential to ensure the correct mixing ratios of reactants, leading to the desired chemical reactions and product consistency.

Control valves are the most common final control elements used in industry today, owing to their versatility and reliability. They find applications in numerous sectors, including: Control valves regulate the flow of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products through pipelines, ensuring safe and efficient transportation and processing. In water treatment plants, control valves manage the flow of water through various treatment stages, ensuring clean and safe water supply. Control valves play a crucial role in power plants, controlling the flow of steam and cooling water to maintain optimal operating conditions and efficiency. Precise control of fluid flow in chemical plants is vital for accurate mixing, reaction control, and product consistency.
The importance of control valves in these industries cannot be overstated. They enhance process efficiency, ensure safety, and contribute to overall operational excellence. Control valves are indispensable in modern industrial processes, providing the necessary control over fluid flow to maintain optimal operating conditions. Their ability to accurately regulate fluids such as gas, oil, water, and steam makes them a critical component in various sectors. With advancements in actuator technology and control systems, control valves continue to evolve, offering even greater precision and reliability in industrial applications. Understanding their operation and components is essential for anyone involved in the field of industrial automation and process control.

