How do Electric Actuators Work?
On this page
Electric actuators play a pivotal role in modern automation, providing precise control and positioning in various applications. Understanding the types of electric actuators and their working principles is essential for anyone involved in industrial automation and process control. Electric actuators come in several types, each designed to meet specific application requirements: These actuators convert rotational motion into linear motion. They are used in applications requiring precise straight-line movement.
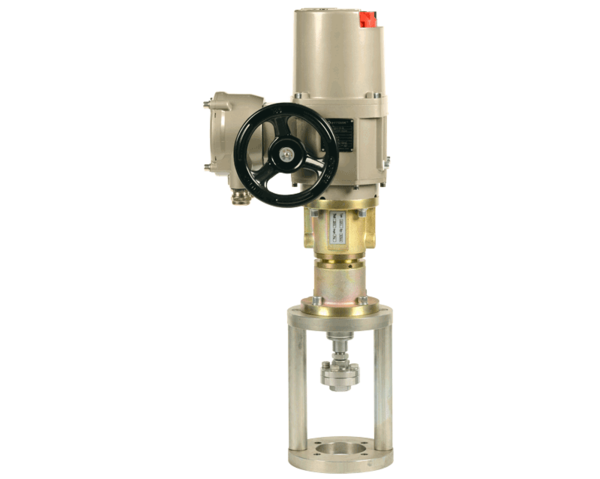
Linear Actuator
These actuators produce rotary motion, making them ideal for applications where rotational movement is needed.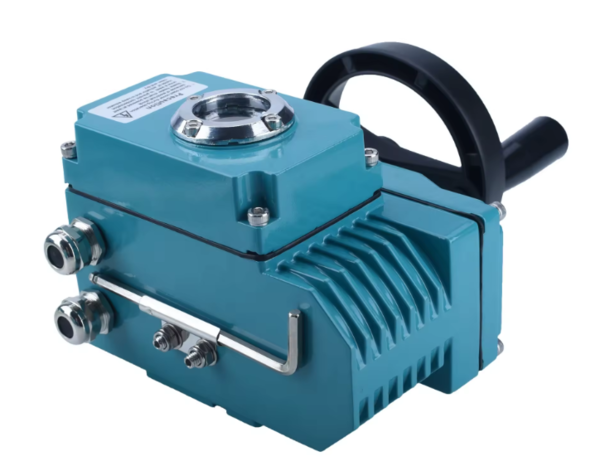 
Rotary Actuator
These use electromagnetic fields to create motion, often used in applications requiring rapid and precise actuation.
These are advanced actuators equipped with feedback systems to provide precise control of position, speed, and torque.
An electric linear actuator is a type of electromechanical device primarily composed of a motor, a set of gears, and a motion mechanism in the form of a worm and tube. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how it works:
The motor is the heart of the actuator, providing the initial rotary motion. When powered, the motor generates rotational energy.
The motor’s rotational energy is transferred to a set of gears. These gears increase the torque while reducing the speed, making the motion more suitable for driving the worm gear.
The worm gear converts the rotational motion into linear motion. As the worm turns, it drives a threaded tube (or nut) along its length, creating linear movement.
The movement of the threaded tube translates into linear motion, which can be used to push, pull, or position loads with high precision. This conversion of rotary motion to linear motion allows electric linear actuators to provide precise and repeatable movements, making them invaluable in applications requiring high accuracy and control. Electric actuators offer several advantages over their pneumatic and hydraulic counterparts: Electric actuators provide superior precision, allowing for exact positioning and control. This precision is particularly beneficial in applications requiring accurate movement and repeatability. Electric actuators have an essentially instantaneous response time, allowing for quick adjustments and real-time control. The design of electric actuators ensures a high degree of stability, minimizing the risk of unwanted movements or fluctuations. Electric actuators can easily be integrated into flexible processes, making them suitable for applications requiring frequent adjustments or reconfigurations. Electric actuators have a lower operating cost compared to pneumatic actuators. The controllers and drivers use low voltage circuitry, resulting in lower power consumption and operational expenses.
In addition to these advantages, electric actuators are also known for their durability and reliability, making them a long-term solution for many industrial applications. Electric actuators are used in a wide range of applications across various industries: In manufacturing, electric actuators are used for precise control of machinery and equipment, ensuring accurate positioning and movement. In the aerospace industry, electric actuators are employed in control surfaces and landing gear systems, where precision and reliability are crucial. Electric actuators are used in automotive applications for controlling various systems such as throttle, braking, and suspension. In medical devices, electric actuators provide precise control for applications such as surgical robots and diagnostic equipment. Electric actuators are integral to robotics, enabling precise movement and control of robotic arms and joints. Electric actuators are essential components in modern automation, offering precise control, stability, and low operating costs. Their ability to convert rotary motion into linear motion with high accuracy makes them indispensable in a wide range of industrial applications. Understanding the different types of electric actuators and their working principles is crucial for optimizing their use in various processes. As technology continues to advance, electric actuators will play an increasingly important role in enhancing the efficiency and precision of automated systems.

