Pneumatic globe control valves are a cornerstone of modern industrial automation, offering precise control of process parameters in pipelines. Unlike electric or hydraulic valves, pneumatic globe valves use compressed air as the driving force. The actuator, typically a cylinder or piston, converts the energy of compressed air into mechanical motion, which then moves the valve to regulate the flow of gases, liquids, or steam.
Pneumatic control valves are widely appreciated for their intrinsic safety, high responsiveness, and simplicity of operation. Because they rely on air pressure rather than electricity, these valves are especially suitable for environments where explosion-proof measures are necessary. Their ability to integrate seamlessly with industrial automation systems, including PLCs and DCS, makes them indispensable in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, water treatment, HVAC, and food processing.
In addition to standard on-off functionality, pneumatic globe control valves provide proportional regulation, adjusting the flow of the medium precisely according to process requirements. This ensures efficiency, safety, and stability in various industrial operations.
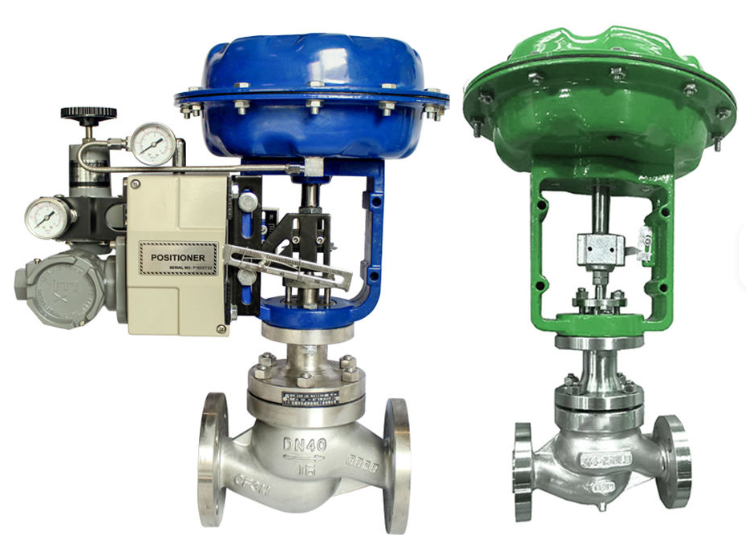

The pneumatic globe control valve generally adopts a right-angle rotary design. This structure allows smooth rotational motion while minimizing wear on the valve components. The right-angle layout also reduces space requirements and facilitates integration with other automation equipment.
One of the key characteristics of a pneumatic globe control valve is its V-shaped valve core. This design is ideal for applications requiring proportional adjustment and high flow capacity. The V-shaped core provides:
High rated flow coefficient (Cv)
Large adjustable ratio (turn-down ratio)
Excellent sealing and minimal leakage
High sensitivity for fine adjustments
Compact design suitable for both vertical and horizontal installation
This makes the valve versatile and capable of handling different types of media, including gas, steam, and liquid, under varying process conditions.
The actuator employs a double-bearing structure, which reduces starting torque and enhances stability. This ensures that the valve responds quickly and accurately to control signals while minimizing wear and tear on moving parts.
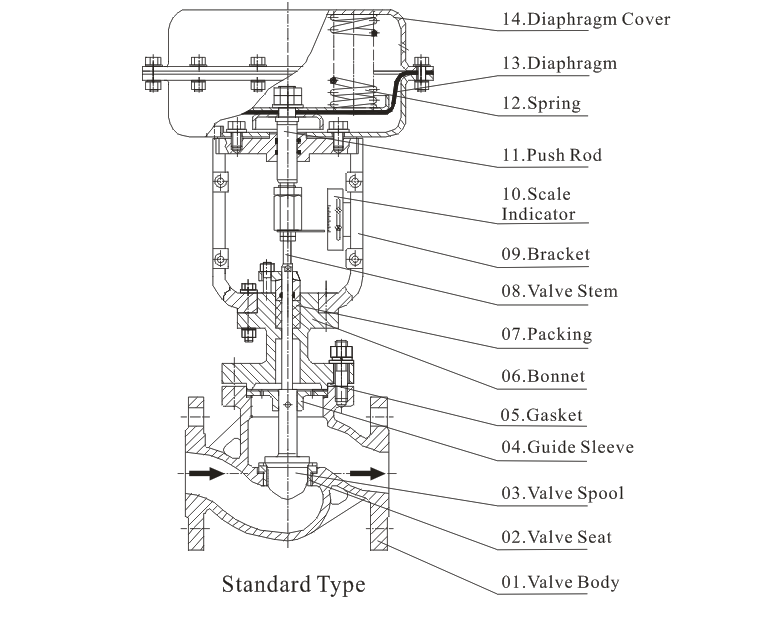
The pneumatic actuator is the driving element of the valve and is responsible for converting compressed air pressure into mechanical motion. The main components include:
Adjusting bolt: Allows fine-tuning of actuator travel and stroke.
Actuator box: Houses internal mechanisms and protects them from environmental factors.
Crank arm: Converts linear piston motion into rotary movement.
Cylinder block and cylinder shaft: Provide structural support and guide piston movement.
Piston: Moves under air pressure to actuate the valve.
Connecting rod and universal shaft: Transfer motion to the valve stem.
By combining these components, pneumatic actuators provide reliable, precise, and fast operation, which is critical for processes requiring continuous flow or pressure control.
Pneumatic globe control valves consist of two main elements: the actuator and the valve body.
Actuator Function: The actuator receives a control signal, usually in the form of air pressure, from the industrial automation system. This pressure generates a thrust force that moves the regulating mechanism.
Valve Body Function: The valve body comes into direct contact with the process medium and controls its flow by opening or closing according to the actuator’s movement.
The combination of these components allows pneumatic globe valves to provide both on-off control and proportional regulation, making them suitable for complex industrial processes.
Advantages of pneumatic globe control valves include:
Fast response time for dynamic process changes
Simple and reliable control mechanisms
Intrinsic safety suitable for explosive or hazardous environments
Accurate proportional adjustment for precise process control
Proper installation is crucial to ensure the performance, safety, and longevity of pneumatic globe control valves. Key considerations include:
Install the valve at a sufficient height above ground.
Provide space above and below the valve for maintenance, inspection, and disassembly.
For valves equipped with handwheels or pneumatic positioners, ensure easy access for operation and observation.
Typically installed on horizontal pipelines but can also be mounted vertically.
Ensure the valve is properly supported to maintain stability.
Horizontal installation on vertical pipelines requires additional support, except for small-diameter valves.
Avoid introducing additional stress to the valve during installation.
Ambient temperature range: -30°C to +60°C
Maximum relative humidity: 95%
Ensure the installation environment does not adversely affect the valve’s materials or pneumatic components.
Install straight pipe sections upstream and downstream of the valve.
Minimum recommended length: 10 times the pipe diameter (10D) to ensure accurate flow characteristics.
Use reducing pipes if the valve diameter differs from the pipeline diameter.
Small-diameter valves may use threaded connections.
Ensure the flow direction arrow on the valve matches the process medium flow.
Bypass piping allows manual operation or switching during maintenance.
Enables valve inspection and overhaul without shutting down the entire system.
Remove foreign materials such as welding slag, dirt, or debris from the pipeline before installation.
Prevents damage to the valve’s internal components and ensures smooth operation.
Pneumatic globe control valves are widely used across various industries due to their reliability and precision.
Control the flow of flammable, corrosive, or toxic liquids and gases.
Maintain precise process conditions for safety and efficiency.
Reduce the risk of leakage or environmental contamination.
Manage steam flow in boilers, turbines, and heat exchangers.
Ensure consistent pressure and temperature for optimal energy efficiency.
Support automatic control systems for precise regulation.
Regulate crude oil, natural gas, or refined product pipelines.
Operate safely in hazardous or explosive environments.
Provide proportional control for process optimization.
Control water flow, chemical dosing, and treatment processes.
Ensure reliability under variable pressures and temperatures.
Facilitate efficient operation of municipal and industrial water systems.
Regulate heating, ventilation, and cooling fluids.
Improve energy efficiency and climate control in large facilities.
Integrate with building automation systems for precise environmental management.
Pneumatic globe control valves offer several advantages over other valve technologies, including:
Faster actuation compared to electric or hydraulic valves
Intrinsic safety in explosive or flammable environments
Proportional control for precise process regulation
Durability and long service life under heavy-duty industrial conditions
Versatility for gases, liquids, and steam
Compact design suitable for installations in restricted spaces
These advantages make pneumatic globe control valves ideal for critical applications where reliability and safety are paramount.
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of pneumatic globe control valves:
Check actuator, valve body, and accessories for wear or damage.
Inspect seals and packing to prevent leaks.
Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
Calibrate positioners periodically to maintain precise proportional control.
Ensure clean, dry, and regulated compressed air supply to prevent actuator damage.
Keep bypass lines and manual operation options functional for emergency situations.
Monitor for air leaks in the actuator system to maintain efficiency and performance.
As industrial automation evolves, pneumatic globe control valves are becoming increasingly integrated with advanced control systems, smart sensors, and IoT-enabled monitoring. Future trends include:
Intelligent valve positioners for real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance
Integration with digital twins to simulate and optimize process control
Energy-efficient actuators that reduce air consumption
Enhanced materials and coatings to improve durability in harsh environments
These innovations will continue to enhance the precision, reliability, and safety of pneumatic globe control valves in complex industrial systems.
Pneumatic globe control valves are vital components for regulating flow, pressure, and temperature in industrial pipelines. With their intrinsic safety, rapid response, and precise proportional control, these valves remain indispensable across chemical, power, oil and gas, water treatment, and HVAC industries. Proper installation, maintenance, and operation are essential to maximizing their performance and lifespan.
As industrial automation advances, pneumatic globe control valves will continue to play a critical role in achieving efficient, safe, and reliable control of process systems. Their versatility, durability, and accuracy make them a reliable choice for engineers and operators worldwide.
