Globe Valves vs Control Valves: What’s the Difference?
On this page
In the realm of industrial piping and flow control, selecting the appropriate valve is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. Among the many types of valves available, globe valves and control valves are two commonly used options. While they may appear similar at first glance, each has unique characteristics and applications. This article delves into the differences between globe valves and control valves, their key features, and the factors to consider when choosing the right valve for your specific needs.
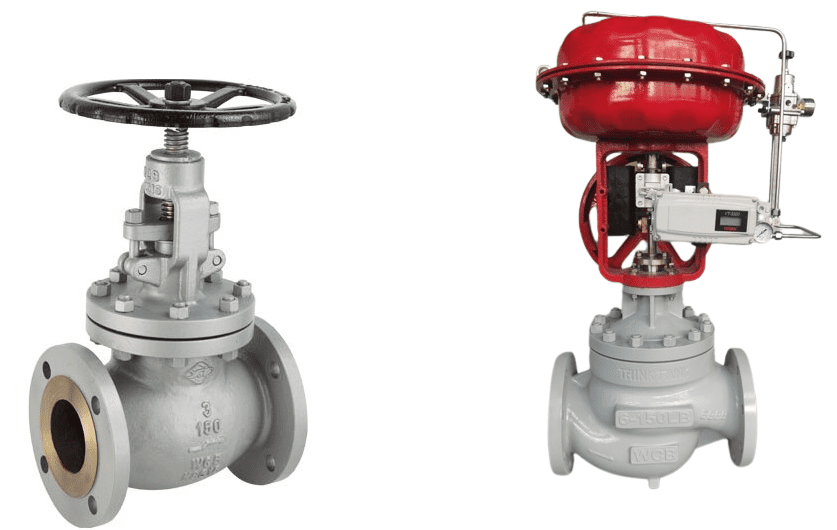
Valves play an integral role in controlling the flow of fluids in various industrial processes. Globe valves and control valves, in particular, are designed to regulate flow, but they do so in distinct ways and are suitable for different applications. Understanding their differences is essential for making an informed decision. A globe valve is a type of valve used to regulate flow in a pipeline. It consists of a movable disc-type element and a stationary ring seat in a generally spherical body. The globe valve derives its name from the globular shape of its body. The body is the main structure of the globe valve, housing all internal components and providing the pathways for fluid flow. The bonnet is a cover on the valve body that holds the stem and other components in place. It is typically bolted or screwed onto the body. The plug or disc is the movable component that regulates flow. It is positioned against or away from the seat to control the passage of fluid. The stem connects the actuator (manual or automatic) to the disc and transmits the motion needed to move the disc. The seat is a stationary component within the valve body that the disc presses against to close the valve. It provides a seal to prevent fluid from passing through when the valve is closed. A control valve is a valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage. It is an essential component in process control systems, providing precise regulation of flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid level.
Control valves are typically operated automatically by actuators and positioned via control signals from an external controller. They are more sophisticated than globe valves and can perform a wider range of functions.
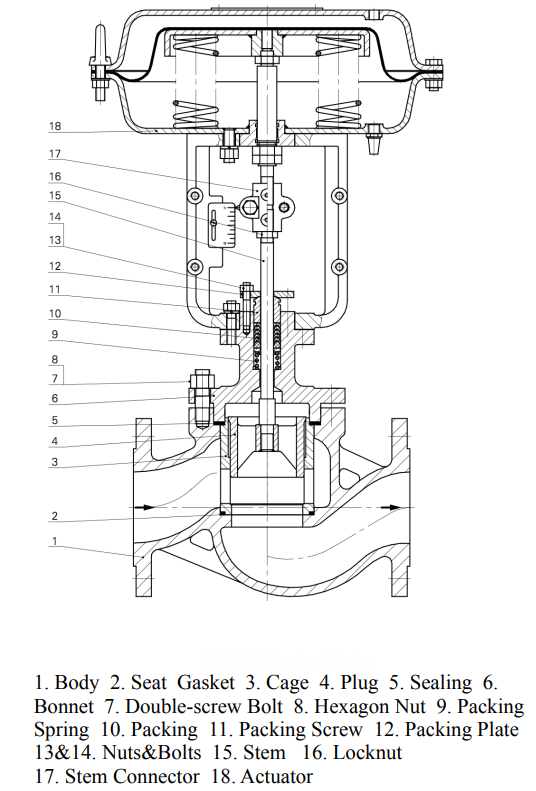 While both globe valves and control valves serve to regulate flow, they differ in their construction, operation, and applications.
Globe valves have a simpler design with a disc and seat mechanism. Control valves, on the other hand, are more complex, incorporating actuators and positioners for automated control.
Globe valves are primarily manually operated, though some can be automated. Control valves are designed for automatic operation and can be precisely controlled via external signals.
Globe valves are commonly used for on-off and throttling applications in pipelines. Control valves are used in more complex process control systems where precise regulation of flow, pressure, or temperature is required.
1. Simple construction and operation.
While both globe valves and control valves serve to regulate flow, they differ in their construction, operation, and applications.
Globe valves have a simpler design with a disc and seat mechanism. Control valves, on the other hand, are more complex, incorporating actuators and positioners for automated control.
Globe valves are primarily manually operated, though some can be automated. Control valves are designed for automatic operation and can be precisely controlled via external signals.
Globe valves are commonly used for on-off and throttling applications in pipelines. Control valves are used in more complex process control systems where precise regulation of flow, pressure, or temperature is required.
1. Simple construction and operation.
2. Suitable for throttling and shut-off applications.
3. Provides good shut-off capabilities.
4. Can handle a variety of fluids, including gases, liquids, and steam. 1. Automatic operation with actuators.
2. High precision in regulating flow, pressure, and temperature.
3. Suitable for complex process control applications.
4. Can be integrated with control systems for remote operation. 1. Water and wastewater treatment.
2. Oil and gas pipelines.
3. Power plants.
4. Chemical processing. 1. Chemical and petrochemical industries.
2. Pharmaceutical manufacturing.
3. Food and beverage production.
4. HVAC systems. 1. Simple design and easy maintenance.
2. Good throttling capability.
3. Effective shut-off performance.
4. Versatile in handling various fluids. 1. Higher pressure drop compared to other valves.
2. Requires manual operation unless automated.
3. Limited to on-off and basic throttling applications. 1. High precision in flow control.
2. Automatic operation reduces the need for manual intervention.
3. Can handle complex process control tasks.
4. Integrates with control systems for advanced functionality. 1. More complex design and higher cost.
2. Requires regular maintenance and calibration.
3. Dependence on external control systems. Selecting the appropriate valve depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your application, the type of fluid being handled, the level of control needed, and budget considerations.
For simple on-off or throttling applications: A globe valve may be sufficient. It offers ease of use, reliability, and effective shut-off capabilities.
For precise flow control in complex systems: A control valve is the better choice. Its ability to automate and integrate with control systems makes it ideal for applications requiring accurate regulation.
Consider the operational environment, pressure and temperature conditions, and the desired level of automation when making your selection. Understanding the differences between globe valves and control valves is essential for selecting the right valve for your specific application. While globe valves offer simplicity and reliability for basic flow control, control valves provide the precision and automation required for complex process control. By considering the features, advantages, and applications of each type, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and efficiency in your industrial operations.

Valves play an integral role in controlling the flow of fluids in various industrial processes. Globe valves and control valves, in particular, are designed to regulate flow, but they do so in distinct ways and are suitable for different applications. Understanding their differences is essential for making an informed decision. A globe valve is a type of valve used to regulate flow in a pipeline. It consists of a movable disc-type element and a stationary ring seat in a generally spherical body. The globe valve derives its name from the globular shape of its body. The body is the main structure of the globe valve, housing all internal components and providing the pathways for fluid flow. The bonnet is a cover on the valve body that holds the stem and other components in place. It is typically bolted or screwed onto the body. The plug or disc is the movable component that regulates flow. It is positioned against or away from the seat to control the passage of fluid. The stem connects the actuator (manual or automatic) to the disc and transmits the motion needed to move the disc. The seat is a stationary component within the valve body that the disc presses against to close the valve. It provides a seal to prevent fluid from passing through when the valve is closed. A control valve is a valve used to control fluid flow by varying the size of the flow passage. It is an essential component in process control systems, providing precise regulation of flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid level.
Control valves are typically operated automatically by actuators and positioned via control signals from an external controller. They are more sophisticated than globe valves and can perform a wider range of functions.
 While both globe valves and control valves serve to regulate flow, they differ in their construction, operation, and applications.
Globe valves have a simpler design with a disc and seat mechanism. Control valves, on the other hand, are more complex, incorporating actuators and positioners for automated control.
Globe valves are primarily manually operated, though some can be automated. Control valves are designed for automatic operation and can be precisely controlled via external signals.
Globe valves are commonly used for on-off and throttling applications in pipelines. Control valves are used in more complex process control systems where precise regulation of flow, pressure, or temperature is required.
1. Simple construction and operation.
While both globe valves and control valves serve to regulate flow, they differ in their construction, operation, and applications.
Globe valves have a simpler design with a disc and seat mechanism. Control valves, on the other hand, are more complex, incorporating actuators and positioners for automated control.
Globe valves are primarily manually operated, though some can be automated. Control valves are designed for automatic operation and can be precisely controlled via external signals.
Globe valves are commonly used for on-off and throttling applications in pipelines. Control valves are used in more complex process control systems where precise regulation of flow, pressure, or temperature is required.
1. Simple construction and operation.2. Suitable for throttling and shut-off applications.
3. Provides good shut-off capabilities.
4. Can handle a variety of fluids, including gases, liquids, and steam. 1. Automatic operation with actuators.
2. High precision in regulating flow, pressure, and temperature.
3. Suitable for complex process control applications.
4. Can be integrated with control systems for remote operation. 1. Water and wastewater treatment.
2. Oil and gas pipelines.
3. Power plants.
4. Chemical processing. 1. Chemical and petrochemical industries.
2. Pharmaceutical manufacturing.
3. Food and beverage production.
4. HVAC systems. 1. Simple design and easy maintenance.
2. Good throttling capability.
3. Effective shut-off performance.
4. Versatile in handling various fluids. 1. Higher pressure drop compared to other valves.
2. Requires manual operation unless automated.
3. Limited to on-off and basic throttling applications. 1. High precision in flow control.
2. Automatic operation reduces the need for manual intervention.
3. Can handle complex process control tasks.
4. Integrates with control systems for advanced functionality. 1. More complex design and higher cost.
2. Requires regular maintenance and calibration.
3. Dependence on external control systems. Selecting the appropriate valve depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of your application, the type of fluid being handled, the level of control needed, and budget considerations.
For simple on-off or throttling applications: A globe valve may be sufficient. It offers ease of use, reliability, and effective shut-off capabilities.
For precise flow control in complex systems: A control valve is the better choice. Its ability to automate and integrate with control systems makes it ideal for applications requiring accurate regulation.
Consider the operational environment, pressure and temperature conditions, and the desired level of automation when making your selection. Understanding the differences between globe valves and control valves is essential for selecting the right valve for your specific application. While globe valves offer simplicity and reliability for basic flow control, control valves provide the precision and automation required for complex process control. By considering the features, advantages, and applications of each type, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and efficiency in your industrial operations.

