In the world of industrial automation, fluid control plays a central role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and precision. Among the many valve technologies available, pneumatic actuated globe valves have earned a reputation as reliable, versatile, and safe components for regulating the flow of liquids, gases, and steam. These valves combine the trusted throttling performance of the traditional globe valve with the responsiveness and automation benefits of a pneumatic actuator, making them an indispensable choice across industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, power generation, and water treatment.
At the heart of their operation, pneumatic actuated globe valves rely on compressed air as a power source. The actuator converts this air pressure into mechanical force, moving the valve stem and plug to modulate flow rates with precision. With the support of accessories like valve positioners, solenoid valves, converters, retaining valves, air filters, and pressure regulators, these valves can function seamlessly as part of a larger process automation system.
What sets pneumatic valves apart from their electric or manual counterparts is their ability to deliver rapid response, intrinsic safety in explosive environments, and reliable performance with minimal maintenance. Their natural “fail-safe” design options (fail-open or fail-closed) provide additional security for critical processes. In industries where downtime, safety incidents, or inefficient flow control could translate to substantial costs, pneumatic actuated globe valves provide the balance of durability, safety, and precise regulation that engineers depend on.
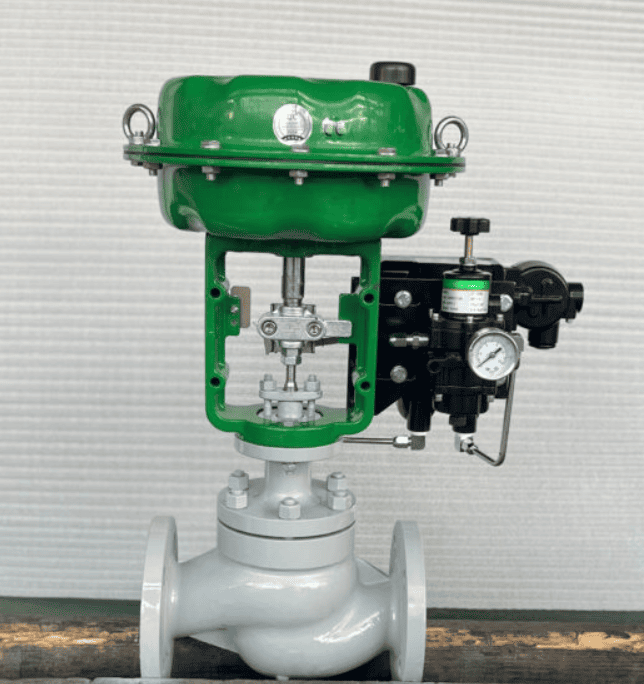
A pneumatic actuated globe valve is an automated control valve that uses compressed air to drive a globe valve mechanism. The globe valve design itself features a movable plug (or disc) that seats against a stationary ring to regulate flow. Unlike ball or butterfly valves, which are better suited for on/off control, globe valves excel in throttling applications where precise flow regulation is needed.
By attaching a pneumatic actuator to this mechanism, the globe valve becomes part of an automated control loop. The actuator receives air pressure signals—often from a valve positioner connected to the plant’s Distributed Control System (DCS)—and translates them into movement of the valve stem. This enables the valve to open, close, or modulate proportionally in real time based on process requirements.
Industries value pneumatic globe valves for their:
Precision: Ideal for regulating flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid levels.
Speed: Pneumatic actuators respond quickly to control signals.
Safety: No sparks or electrical components, making them safe in explosive atmospheres.
Durability: Few moving parts, minimizing wear and tear.
In short, a pneumatic globe valve combines the best of traditional valve engineering with the advantages of modern automation.
One of the main advantages of choosing a pneumatic globe valve is ease of operation. Manual valves require physical effort and on-site operation, but pneumatic actuators allow remote operation with the push of a button or an automated control signal. Operators can manage valves from a central control room, reducing the need for exposure to hazardous or hard-to-reach environments.
In addition, advanced accessories such as solenoid valves, limit switches, and positioners can be integrated for even more accurate operation. This allows the valve not only to open and close but also to hold intermediate positions with high precision. Automation enables consistent process quality and frees operators from repetitive manual tasks, improving both safety and productivity.
Maintenance costs are a constant concern in industrial operations. Pneumatic globe valves excel in this area thanks to their simple design and fewer wear-prone parts compared with electric or hydraulic actuators.
Compressed air as a power source eliminates the risks associated with electrical wiring, reducing potential points of failure.
Pneumatic actuators avoid oil leaks or hydraulic fluid contamination, making them cleaner and environmentally friendlier.
Because air has natural cushioning properties, actuators experience less mechanical shock, reducing wear on valve internals.
The combination of simple mechanics and clean operation makes pneumatic globe valves easier and less expensive to maintain over long service lifetimes.
In industries where hazardous fluids, gases, or high pressures are common, safety is paramount. Pneumatic actuated globe valves are designed with safety in mind.
They shut off quickly and securely in emergency situations, minimizing the risk of leaks or spills.
Fail-safe configurations (spring-return actuators) ensure the valve automatically closes or opens to a safe position during power or air supply loss.
Operators remain at a safe distance, reducing human exposure to dangerous environments.
This makes pneumatic globe valves especially valuable in oil refineries, chemical plants, and power generation facilities, where even minor leaks can have severe consequences.
The precise throttling capability of a globe valve combined with the fast, reliable actuation of pneumatic power allows for superior process control.
Accurate positioning ensures stable flow regulation, critical in maintaining product quality.
Integration with sensors and control systems enables real-time adjustments for flow, pressure, or temperature changes.
Automated operation allows coordination across multiple systems, optimizing efficiency in complex industrial networks.
For industries like chemical processing, where maintaining tight tolerances in pressure and temperature is essential, pneumatic actuated globe valves provide the reliability needed for optimal results.
Pneumatic actuated globe valves are used across a wide range of industries due to their versatility:
Oil and Gas: Controlling steam, gas, or crude oil flows in upstream, midstream, and downstream operations.
Chemical Processing: Regulating aggressive chemicals under varying temperatures and pressures.
Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring sterile and precise fluid control for manufacturing processes.
Power Generation: Controlling steam and cooling water in thermal and nuclear power plants.
Water Treatment: Managing flow and pressure in desalination plants, municipal systems, and wastewater treatment facilities.
Pulp and Paper: Controlling steam and chemical dosing for paper production.
In each of these applications, the ability to combine safety, precision, and automation makes pneumatic globe valves a preferred choice.
When selecting a pneumatic actuated globe valve, several factors should be considered:
Valve Size and Pressure Rating: Match the valve to pipeline specifications.
Body Material: Choose materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, or exotic alloys depending on the fluid’s corrosiveness and temperature.
Actuator Type: Spring-return for fail-safe operation or double-acting for balanced control.
Accessories: Positioners, solenoid valves, and air filter regulators can enhance control and reliability.
Flow Characteristics: Select the appropriate trim design for linear or equal-percentage flow control.
Industry Standards: Ensure compliance with standards like API, ANSI, or ISO, depending on the application.
By carefully considering these aspects, plant engineers can ensure long-term reliability and efficiency.
With the rise of Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing, pneumatic actuated globe valves are also evolving. Modern trends include:
Smart Positioners: Enabling digital communication (HART, Fieldbus, or Profibus) for better integration with automation systems.
Energy Efficiency: Development of low air-consumption actuators to reduce operating costs.
Advanced Materials: Use of corrosion-resistant alloys and coatings for longer service life in harsh environments.
Predictive Maintenance: Sensors and monitoring systems to track valve health and predict failures before they occur.
These innovations will continue to improve reliability, reduce downtime, and enhance process optimization.
The pneumatic actuated globe valve is more than just a flow control device—it is a critical component in modern industrial systems where precision, safety, and efficiency are essential. Its ability to combine the throttling capabilities of a globe valve with the automation and reliability of a pneumatic actuator makes it a trusted choice across diverse industries.
From reduced maintenance costs and increased safety to enhanced process control and ease of operation, these valves offer clear advantages over manual or electric alternatives. As industries adopt smarter, more connected technologies, pneumatic actuated globe valves will remain a cornerstone of reliable process automation, evolving with new materials, designs, and digital integration.
In an industrial world where every second of uptime matters, pneumatic actuated globe valves stand out as dependable workhorses—ensuring smooth, safe, and optimized operation for years to come.
