Understanding Flow Control Valves: A Comprehensive Insight
On this page
Flow control valves serve as the silent guardians of fluid systems, orchestrating the delicate balance between flow rate, pressure, and system stability. Yet, their inner workings remain shrouded in mystery for many. In this illuminating exploration, we unravel the intricate mechanics behind these indispensable components, shedding light on their operation and significance across diverse industries.
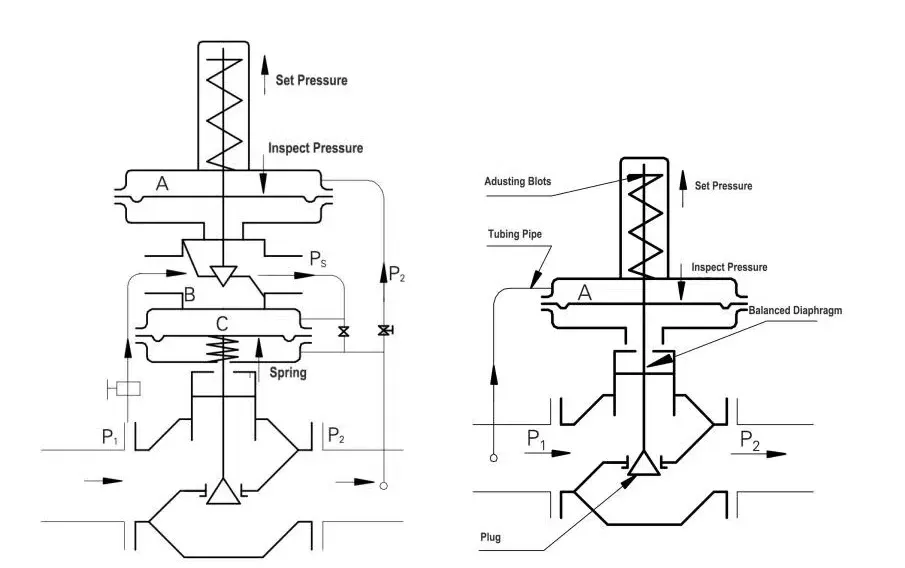

Drawing of Pressure Reducing Regulator
At its core, a flow control valve is a mechanical device designed to regulate the rate of fluid flow within a system. From simple household plumbing fixtures to complex industrial pipelines, these valves play a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and efficiency. The fundamental principle governing the operation of flow control valves is the restriction of flow through an adjustable orifice. By manipulating the size of the orifice, these valves can modulate the flow rate of liquids, gases, or steam with remarkable precision.
One of the most common types of flow control valves is the globe valve, characterized by its spherical body and linear motion stem. When the valve is in the open position, fluid flows freely through the valve body, unrestricted by the valve seat. However, as the stem is rotated or linearly displaced, the valve seat gradually constricts the flow path, regulating the flow rate accordingly.
Another widely used variety is the butterfly valve, distinguished by its disc-shaped closure element. In the open position, the disc aligns with the flow direction, allowing unimpeded passage of fluid. By rotating the disc perpendicular to the flow, the valve can be closed partially or completely, exerting precise control over the flow rate.
The mechanics of flow control valves are further refined through the integration of actuators, which automate the valve's operation. Electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators translate external signals into mechanical motion, allowing for remote control and precise adjustments based on real-time conditions.
In addition to regulating flow rate, flow control valves also play a vital role in maintaining system stability and safety. By modulating flow, these valves can prevent excessive pressure buildup, alleviate water hammer effects, and protect downstream equipment from damage.
The significance of flow control valves extends across a myriad of industries, ranging from oil and gas to water treatment and beyond. In oil refineries, for instance, these valves are used to regulate the flow of crude oil, process fluids, and gases throughout the refining process, ensuring optimal product quality and operational efficiency.
In municipal water distribution systems, flow control valves help maintain steady water pressure, prevent backflow, and facilitate the efficient allocation of water resources.
Similarly, in HVAC systems, these valves regulate the flow of chilled or heated water to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and energy efficiency.
As technological advancements continue to drive innovation in fluid systems, the role of flow control valves will only grow in importance. From smart valves equipped with sensors and actuators to advanced materials engineered for durability and reliability, the future holds boundless possibilities for enhancing the performance and functionality of these indispensable components.
In conclusion, flow control valves serve as the linchpin of fluid systems, balancing the demands of flow rate, pressure, and system stability with unparalleled precision. Through a deeper understanding of their mechanics and significance, we can harness the full potential of these essential components to drive progress and innovation across industries.
